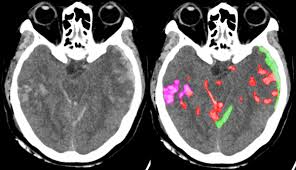
Source: physicsworld.com Head CT is used worldwide to assess neurological emergencies and detect acute brain haemorrhages. Interpreting these head CT scans requires readers to identify tiny subtle abnormalities, with near-perfect sensitivity, within a 3D stack of greyscale images characterized by poor soft-tissue contrast, low signal-to-noise ratio and a high incidence of artefacts. As such, even Read More
Tag: emergencies
Upgrade & Secure Your Future with DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps, MLOps!
We spend hours on Instagram and YouTube and waste money on coffee and fast food, but won’t spend 30 minutes a day learning skills to boost our careers.
Master in DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps & MLOps!
Learn from Guru Rajesh Kumar and double your salary in just one year.