In WordPress, roles and capabilities are crucial for maintaining security and managing user access to different functionalities of your website. They essentially create a hierarchy of users with varying levels of control.
Capabilities define specific actions a user can perform on the site, like writing posts, editing content, installing plugins, or managing other users. Roles group these capabilities together, making it easier to assign permission levels.
Here’s why this system is important:
- Security: By restricting access to sensitive actions like installing plugins or editing themes, you minimize the risk of accidental or malicious damage to your site.
- Content Management: You can delegate tasks efficiently. For instance, assign editor privileges to users who manage content created by others, while authors can focus on writing their own posts.
- Workflow Efficiency: Roles streamline your workflow. Contributors can write drafts without publishing them directly, allowing editors to review and publish content.
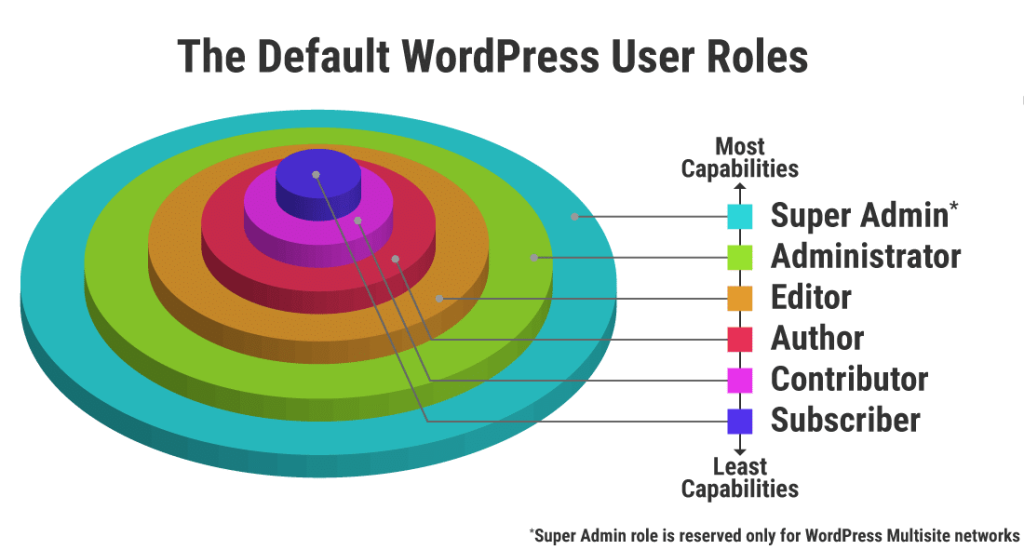
Let’s break down the main default user roles in WordPress:
- Super Admin:
This role has full control over everything in the site, including adding new users, creating new roles, and managing all content. There should typically only be one Super Admin for a WordPress site.
2. Administrator:
- Significance: Administrators have full control over the WordPress site. They can create, delete, and manage users, as well as install plugins and themes, edit core files, and modify any content. Essentially, they have unrestricted access to all features and settings.
- Use cases: Administrators are typically the site owners or trusted individuals responsible for site management, configuration, and overall functionality.
3. Editor:
- Significance: Editors have control over content management. They can publish, edit, or delete any post or page, including those created by other users. However, they cannot modify site settings, install plugins/themes, or perform administrative tasks.
- Use cases: Editors are often senior staff or content managers responsible for overseeing content quality and ensuring consistency across the site.
4. Author:
- Significance: Authors have the ability to write, edit, and publish their own posts. They cannot modify or delete posts created by other users, nor can they access site settings or perform administrative tasks.
- Use cases: Authors are typically individual contributors or guest bloggers who contribute content to the site on a regular basis.
5. Contributor:
- Significance: Contributors can write and edit their own posts, but they cannot publish them. Instead, their posts must be reviewed and published by an Editor or Administrator. They also cannot edit or delete posts created by other users.
- Use cases: Contributors are often freelance writers, guest bloggers, or users who contribute occasional content to the site but don’t require full publishing privileges.
6. Subscriber:
- Significance: Subscribers have the most limited role. They can only manage their profile and subscribe to updates from the site. They cannot create, edit, publish, or delete any content.
- Use cases: Subscribers are typically users who register on the site to receive updates or access restricted content, such as members of a community or subscribers to a newsletter.
Roles and capabilities in WordPress are crucial for maintaining site security, managing user access, and facilitating collaboration. By assigning appropriate roles to users, site owners can ensure that each individual has the necessary permissions to fulfill their responsibilities without granting unnecessary access that could compromise site integrity or privacy.